Basic Facts You Need to Know About Shrimp
Shrimp is a valuable aquatic food and excellent protein source for human consumption. So, shrimp hatchery is very popular in many countries.
The main parts of the shrimp can identify in the below picture.
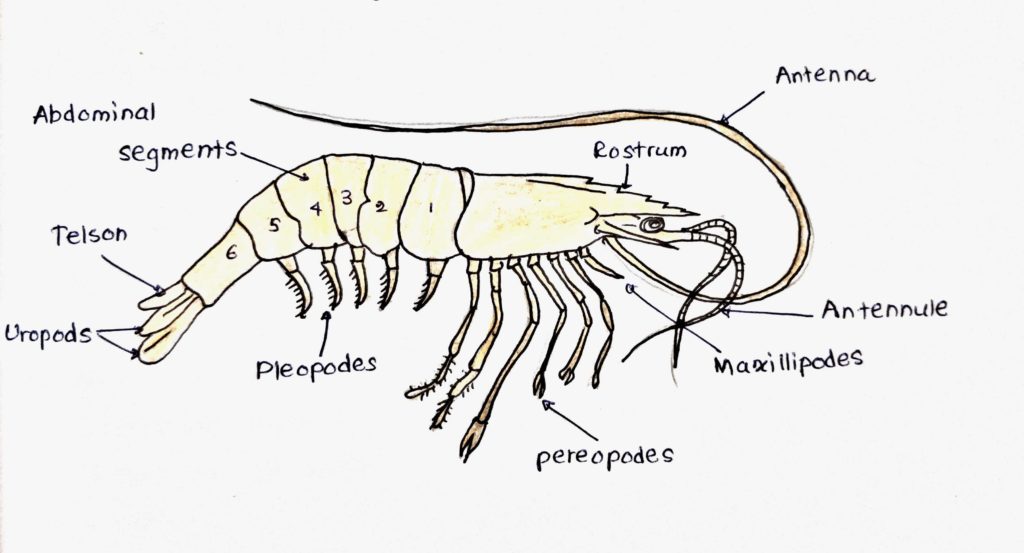
For your extra knowledge, following are some of the important considerations that must take into account
when choosing the site for shrimp hatchery process.
Site Selection
- Electric power availability
- Ease of access to the site
- Availability of sea water and fresh water
Shrimp hatchery meaning
Hatchery is a process or an establishment where eggs hatched under particular conditions. There is also a method called brine shrimp hatchery. But the normal process is discussed in this article.
Shrimp Hatchery Process and Technology
Shrimp hatchery practice can divide into 3 main categories based on the hatchery size. They are small-scale, medium-scale and large-scale. We are going to discuss common practice in this article. The hatchery management system consists of 6 units. They are,
- Quarantine unit
- Maturation unit
- Spawning unit
- Hatchering unit
- Larval raring unit
- Nursery
Let’s discuss one by one.
1.Quarantine unit
A quarantine unit is simply a small tank designed to isolate a fish. In this scenario, they hold in a particular area called Quarantine Unit after the capture of adult shrimps from the water before being transferred to the other units. The purpose of this restriction is to verify whether the broodstock(a group of mature individuals) is having diseases because they can directly affect the economy of shrimp farmers.
Disease examination, treatment for curable diseases and remove infected broodstock are the main functions of this unit. It situated away from other units as it is a high-risk area.
Following tests execute in order to examine diseases.
MBV test (Monodon Baculovirus)
- This test is unique and also a widely reported virus for shrimps. Check the presence or absence of Monodon Baculovirus infection. This virus mainly affects on Pl 20-30 of shrimps. We use feces or stool samples of shrimps to perform this test. The severity of the infection enhanced by poor husbandry and crowding condition in the unit.
PCR test (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
- This technique is popular in veterinary research. The aim of this test is to detect White Spot Syndrome Virus(WSSV) detection. Normally 5th pleopode is cut and the muscles of it are used to perform PCR test
We use Anti fungal and antimicrobial chemicals here. After confirming the healthiness of broodstock, we transfer it into the maturation tanks. Before that, they should wash with 200ppm formalin for about 10 minutes.
2.Maturation Unit
Maturation tank is circular with 3-6m in diameter, depth from 1m to 2m and the surface should dark blue or black. And maturation tank can be rectangular and oval shape also. But most common shape is a circular shape. Seawater should filled up to 1m in height. The continuous flow of seawater must ensure. The following optimal conditions should maintain.
- Good water quality
- Dim light or dark environment
- Fresh and nutrient diet
- Silence to minimize stress
A submersible torchlight can use to check whether the female becomes pregnant and mate. So, no need to do eye ablation if they mature properly. Usually, matting occurs in the night time. The sperms stocked in spermatophores of the female. Keeping ablated shrimp in maturation tanks will ensure a continuous supply of gravid females. Eye ablationHormones responsible for gonad inhibition contain in eyes, and those drain through the stalk of the eye. To include the ovaries and testes to form the gonad, the inhibition should remove by preventing the drainage of the hormones stored in the eye. That process is called eye ablation. Eyes act as an endocrine organ in shrimp.
Usually, eye ablation is done early in the morning and late evening in cold water to reduce bleeding. After eye ablation, we treat shrimps for a few hours using antifungal and antimicrobial chemical compounds.
3. Spawning Unit
The spawning unit consist of fiberglass with a gel coat of interior food grade. Mature mated female shrimps should keep in these small tanks which the volume is about 150 litres. The tanks used for housing the gravid females temporarily before they spawn. We place one female per each tank. Typically, spawning occurs around 8 pm-4 am.
2-5 hours after spawning, the female shrimp should remove, and a net can use to collect eggs. 2/3 of water in the tank should remove before collecting eggs. Then we keep those eggs in hatching containers. The remaining water should filter with a 500um sized net in order to remove tissue particles. Then eggs should wash from seawater.
4. Hatching Unit
Washed eggs are then introduced into hatching tanks. Normally one million of eggs can stock in one hatching tank. After 8 hours, eggs are hatched and Nauplii come out from eggs. NI to NIV are grown in these tanks and these stages never feed on meals but from egg yolk, spend about 48 hours.
Nauplii are phototatic and can identify by using light. Switch on the light after hatching process and all nauplii come towards the light. They can collect using nets and then transferred into Larval Raring unit.
5. Larval Raring Unit
Nauplii are stored up to the post-larval stage. These units are easy to clean, drainage and harvest. No usage of operating and security methods and the capacity of a tank is 5000L. These tanks are cylindroconical and made up from fibreglass consist of a centrally located pipe which act as an outlet consisting of fine mesh.
First we add 1/4 of water to the tank and then add 4ppm EDTA. Then we should add antifungal agent. At last, Nauplii are transferred, and the water level is increased. Different larval stages are changed from one tank to another using a scoop net. The larval raring tank is also consisting of green/ brown algae.
6. Nursery Unit
Tanks are circular, square-shaped or rectangular and formed by fibreglass or concrete with an inner plastic line. PL3-PL5 stages in larval rearing unit are harvested and transferred into nursery units.
Stocking density is less to prevent from diseases. The tanks have proper aeration and water drainage system. PL10-PL25 larvae or broodstock can harvest in order to stock at the farm.
Conclusion
We hope you got some knowledge from this article. We used lots of resources to make this article better. But you may find mistakes. Please don’t hesitate to inform them in the below comment section.





